How to Disseminate Maternal Health Information to Rural Women
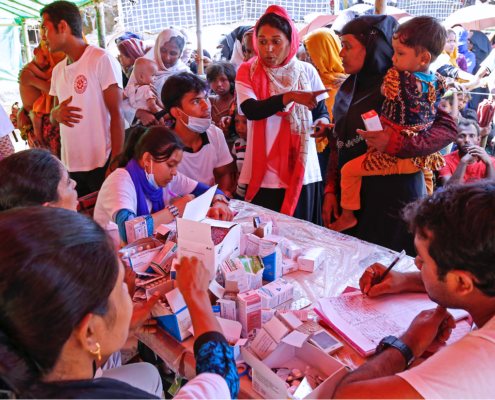
There are numerous ICT projects that focus on maternal health, many designed to reach women in rural areas where there is a severe lack of healthcare services. Mhealth in particular – the use of mobile phones to improve health – has taken off as a tool for providing critical information to pregnant and new mothers. In USAID’s MAMA project, for example, pregnant women in Bangladesh receive weekly information updates via text or voice message.
But what is the best method for disseminating health information to rural women? How can the women learn and interpret the information in a way in which they can understand its value, making certain behavior changes if needed? Vikram Parmar, a professor at the Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands, attempted to find this out through research conducted in India with 120 women from seven different rural villages. Parmar wanted to know how to motivate users of a Primary Health Information System (PHIS) to adopt positive health practices through designing and developing a Health Information System that maximized information dissemination.
Parmar wanted to explore how to improve information dissemination where health ICT projects had fallen short in three areas. First, he was concerned with the limited impact of Health Information Systems in educating rural users, as well as ICT-based health interventions such as film showings and radio program broadcasts that had not improved the health practices of rural target audiences. Secondly, the typical content and design of Health Information Systems did not encourage regular use due to the “non-persuasive setting of health interventions,” resulting in an information gap between rural women and primary health information. Finally, HIS deployed to rural users were based on content developed for urban users, resulting in a mismatch between the information given to rural women and the information they actually needed. In particular, maternal health and other personal women’s health issues had not been addressed.
Parmar proposed addressing these problems by employing a user-centered design framework to develop ICT interventions (see framework in full below). He tested this framework in the context of the PHIS. The results of his exploratory research indicated that the rural women’s knowledge had improved after interacting with the PHIS, signifying the importance of understanding user needs, taking into account existing social beliefs and practices related to health issues. Using this framework could improve information dissemination, resulting in positive change in rural women’s health-related practices.